How to Boost Your Immunity at Home: Tips to Naturally Help Your Body Resist Diseases

Understanding Our Immune System and How the Body Resists Diseases
Our body does not just sit back and watch itself being taken over by disease-causing agents like pathogens or inflammation. Each time anything tries to enter your body and cause you sickness, there is always a resistance within your system that you are not aware of. You only fall sick when an infectious agent wins the fight against your body.
What is Immunity?
The ability of our body to fight back or resist disease-causing agents is known as immunity. In a formal sense, immunity is the state in which the body can resist a noxious agent such as pathogens, processes, or any foreign agent that can cause infectious disease.
The Immune System
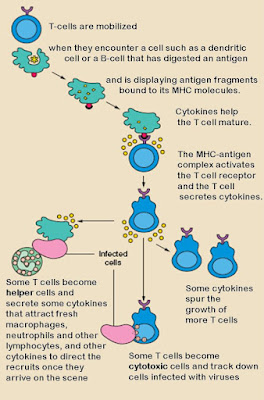
The process of immunity is complex and controlled by the entire immune system. Components of the immune system include antibodies, white blood cells, bone marrow, lymphatic system, thymus, and spleen. However, antibodies and white blood cells are vital and key players in the body's active immunity.
What are antibodies
Antibodies also known as Immunoglobulins are Y-shaped cells within the body that can recognize disease-causing agents like bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens and then engage in the fight against them thereby helping our body resist infections. Antibodies are of five types which include immunoglobulin A, D, E, G, and M (IgA, IgD, IgG IgE, and IgM) which are all isotopes. Antibodies are produced by B-cells, a form of white blood cells created in the bone marrow.
Besides the antibodies that function within our cellular system, and tissues, there are also other natural defense mechanisms like our physical protection such as the skin, mucus membrane, and enzymes.
Types of Immunity
There are three main types of immunity which include adaptive, passive, and innate immunities.
- Adaptive or Active Immunity: Adaptive immunity, also referred to as active immunity is the type of body immunity resulting from exposure to disease-causing agents. Our body can develop resistance to disease after it has been exposed to that disease before. This immunity can be developed through vaccines or the environment we find ourselves.
When you get infected by a certain organism, your body can recognize that disease and produce memory cells to enable it to enable a fight-back next time. This is the main type of immunity mediated by antibodies like B and T cells.
These antibodies circulate in our bodies to keep us healthy and then multiply once they observe a foreign body that might cause diseases.
- Passive Immunity: This is also known as acquired immunity. It is a resistance to diseases resulting from acquisition from other sources. Examples of this type of immunity are when a baby develops resistance to disease because of the antibodies in the mother's milk or within the blood circulation of the placenta. One can also have passive immunity medically such as immunoglobulin injection.
Passive or acquired immunity is temporary and its impact does not last long.
There are two types of acquired immunity which are natural or artificial immunities. While naturally acquired immunity is developed through exposure to natural pathogens, artificially acquired immunity is artificially introduced and it is what is known as immunization.
Immunization is the process of introducing a vaccine ( a suspension of artificially modified disease-causing agents also known as antigens) into the body to boost antibody production against infectious or malignant diseases.
- Innate immunity: Innate immunity is the ability of our body to resist infections because of certain protective features, both externally and internally. For instance, our skin protects our inner body from being exposed to infections around, and our cells naturally fight back when an external agent gets into the body. Everyone is born with this kind of immunity right from childhood. So, this term refers to the generalized body protection against diseases, not specialized immunity as the active immunity that is mediated by B and T cells. Cells that take part in innate immunity include monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, basophils, natural killer cells, etc.
Despite the ability of the body to naturally resist disease, several things can cause our immune system to compromise. Those things that can cause the immune system to become weak include poor diet, certain drugs, smoking, aging, and immunocompromised conditions resulting from diseases like HIV and flu virus, among others.
Natural Ways to Boost Immunity and Resist Diseases Even at Home
While the immune system is functional from birth, there is a need to engage in habits that help boost the effectiveness of the antibodies to fight disease-causing agents and processes like inflammation. In this article, we want to highlight the natural ways that you can boost your immune system to help your body resist diseases even without medicines like vaccines.
The following are natural ways to boost your general immunity and help your body resist diseases:
1. Engage in regular physical exercise
Exercise and other forms of Aerobic physical activity are important for boosting our immune system, according to research. The ability of exercise to perform this function is because exercise helps control the body weight, and helps keep the body fit thereby hindering inflammation and improving the effectiveness of the antibodies. Exercise has so many benefits that engaging in it regularly even at home is mandatory.
2. Eat immune-boosting diet
Some foods we eat are known to help boost the immune system. Food like garlic is known to be a natural T-cell booster. This means that it's able to stimulate the antibodies that fight viruses in the body. Also, some carotene-containing foods like carrots are antioxidants that help the body fight inflammation.
Probiotics like yogurts are also great for boosting our body's defense. You also need foods that contain vitamins C, D, and E. These foods range from fruits and vegetables to nuts or other sources of vitamins and healthy fat.
In other words, having a good eating habit with a well-balanced diet is a great way to boost your immune system and help your body fight disease naturally. So, when next you cook at home, remember that you have to boost your immune system.
3. Sleep well and have enough rest
Lack of sleep and sufficient rest negatively affects our health and does great harm to the immune system. Sleeplessness increases the chance of one developing health disorders including obesity and malignancy which in turn affect the entire body system including our immunity. It might be a busy day at work, but when you get home, remember to take a nap to improve the power of your immune system.
4. Expose yourself to the sunlight regularly
Sunlight is very good for the body. It is the main natural source of vitamin D, although this wonderful vitamin can also be obtained from food. Vitamin D is known for its immunomodulatory effects which help in activating and enhancing the movement of the immune cells and vital antibodies. For those in the tropics, this is naturally not a challenge. However, if you live in other regions of the world, find time at home to expose your body to the magical power of the sunlight.
5. Avoid excess alcoholic drinks
Moderate alcohol may not pose a major threat to our immune system. However, large amounts of alcohol and long-term intake are detrimental to our whole body, and our body's defense can be affected.
One obvious way alcohol consumption can impede our immunity is its ability to interfere with the ciliary function in the upper respiratory system which is meant to filter air into the lungs. This exposes one to diseases like pneumonia and acute respiratory stress disorder (ARDS).
A study published in the National Library of Medicine suggests that alcohol can kill neutrophils and T-cells as well as disrupt antigen-antibody communication which inhibits immune response to antigens. Alcohol can also affect the body's microflora, most of which have some defensive functions on our body.
If you have a cupboard filled with alcohol at home, maybe it is time to replace the drinks with fruits and healthy food.
6. Stop smoking
Smoking is very bad for our entire health. Besides the fact that it can damage the lungs and intoxicate the liver, it is harmful to our immune system. Immune-related disorders like rheumatoid arthritis are known to have an association with smoking. Do not smoke at home, work or anywhere it is known to be harmful to your immunity.
7. Drink sufficient water regularly
Water is the main solvent in our body. Besides helping in the transportation of nutrients, hormones, enzymes, and other useful biochemicals, it is also the main medium for the removal of toxins from our cells through excretion.
In addition, taking sufficient water enhances the activities of antibodies which are only active in aqueous and optimum conditions. Even the mucus membranes which are vital for the body's defense against strange bodies have to remain moist, all thanks to water. This makes water very important for the body's immunity and defense against bacteria, toxins, and other disease-causing agents. Learn to drum enough water at home and carry a bottle of water when you are out.
8. Reduce how you stress yourself
Emotional stress and anxiety are known to cause some disorders such as abdominal pain and heart diseases. However, it was discovered that those who face chronic stress at home (in the family or relationships) or work have their immune system going down gradually.
9. Keep yourself warm
Even without much emphasis, there is a significant rise in flu, common cold, and other cold-enhanced infections during the winter. It seems our body can compromise when the temperature is not friendly. Wearing a coat keeps your body warm and helps it maintain an optimum temperature that can enhance our immunity. When you are at home, learn to minimize your air conditioner and keep some warm.
10. Stick to hygienic lifestyle and sanitary routines
Prevention is better than cure. Even when we have strong immunity naturally, exposing ourselves to diseases or foreign antigens still poses a great threat to our immune system. It is therefore good to wash your hands regularly, live a hygienic lifestyle at home, and avoid transmittable disease. For instance, sharing unsterilized sharp objects or engaging in unprotected sex can get one infected with HIV which is an immune suppression disease.
Summary and conclusion
Our body is designed to defend itself against diseases and their agents. Without such immunity, we would be falling sick all the time. Even when this is a natural process, we can also help to enhance the effectiveness of our antibodies and other resistant mechanisms to boost our immunity. Some of these activities and lifestyles are sustainable while you are at home or work.